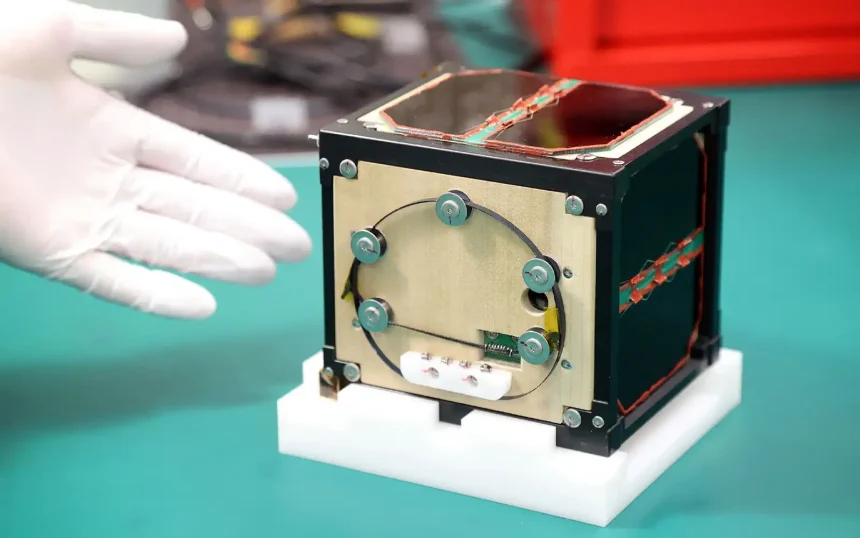
LignoSat: A Milestone in Sustainable Space Materials
In a groundbreaking move, Japanese researchers have launched the world’s first wood-panelled satellite, named LignoSat, to explore timber’s potential as a renewable building material in space. The satellite, weighing just 900 grams, will test the durability and performance of wood in the harsh conditions of space, opening up possibilities for future exploration missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
A Unique Construction: Timber Panels without Screws or Glue
LignoSat’s design is as innovative as its purpose. The satellite’s panels are made from the magnolia tree, selected for its strength and resilience, using a traditional Japanese technique that avoids screws or glue. This method preserves the integrity of the wood and aligns with the researchers’ commitment to using eco-friendly materials. The project’s success could pave the way for timber’s use in space exploration, potentially replacing some of the metals that are commonly used.
Destination ISS: LignoSat’s Journey Begins
LignoSat is on its way to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard a SpaceX mission, from where it will soon be released into orbit. For six months, the satellite will circle the Earth, gathering critical data through sensors that monitor how its wooden panels respond to cosmic radiation, temperature extremes, and vacuum conditions. Researchers are particularly interested in observing any changes in the wood’s structure or integrity during this period.
Testing Timber’s Limits in Space
As LignoSat orbits Earth, its onboard sensors will measure how well the wood withstands the unique environment of space. By analyzing these data, scientists hope to understand if timber could replace certain metals in future spacecraft. Wood’s renewable and lightweight properties make it an appealing option, particularly for building sustainable infrastructure on the Moon or Mars, where resources will be limited, and environmental impacts are a major consideration.
The Future of Sustainable Space Exploration
LignoSat represents an important step toward developing eco-friendly technologies for space exploration. By experimenting with renewable materials like wood, researchers aim to reduce the environmental impact of future missions and reduce dependence on metals, which can be both resource-intensive and costly to produce. If successful, this innovative approach could lead to the development of sustainable habitats and vehicles for long-term missions.
Beyond Earth: Timber’s Potential on the Moon and Mars
The success of LignoSat could have significant implications for future space exploration. If wood proves to be a viable material, it could be used for constructing bases, satellites, or equipment on the Moon or Mars, where reusing and repurposing resources is essential. Such an achievement would not only enhance sustainability but could also simplify the logistics of space missions, making structures lighter and more efficient.
A New Era of Eco-Friendly Space Technology
As LignoSat embarks on its six-month journey, scientists and environmental advocates alike are watching closely. This experiment is more than a test of wood’s resilience—it’s a glimpse into the future of sustainable space technology. With the growing push for eco-friendly materials on Earth, LignoSat’s mission could mark the beginning of an era where our journey to the stars becomes as sustainable as it is innovative.
Also learn about Japan’s New Traffic Laws: Jail Time and Fines for Cyclists on Phones and Riding Under Influence.